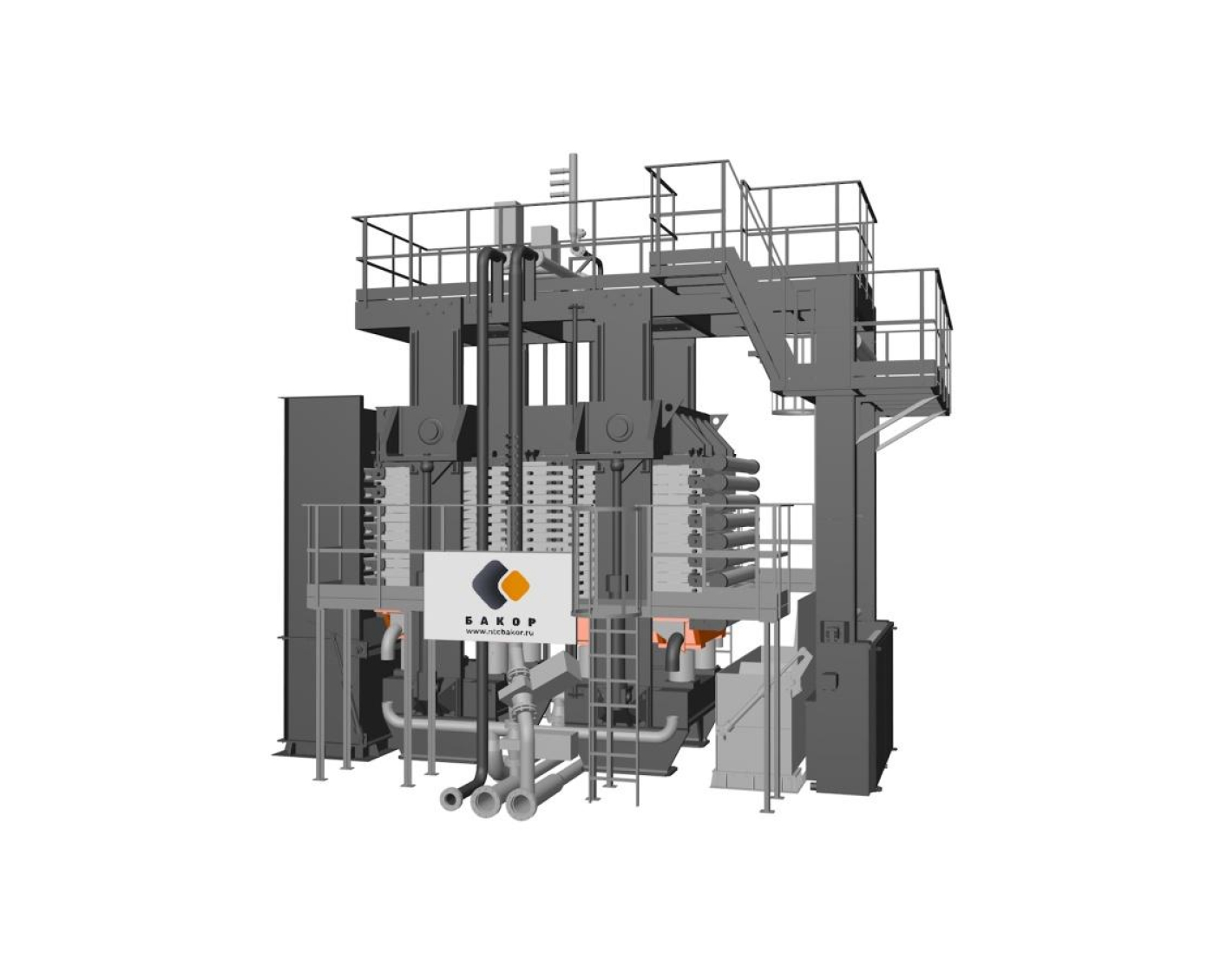
Intended use: Filtration (dewatering) of highly dispersed suspensions (pulps):
Industries:
Applications:
The filters are used for filtering a wide range of suspension classes and are suitable for separation of suspensions with small solids concentrations and high-temperature suspensions that can't be cooled due to crystal crashing out.
Main advantages:
Filtration, washing and air purging processes in one unit in automatic mode according to pre-programmed algorithms
Minimum time of auxiliary operations (filter cloth regeneration and dewatered sludge discharge are combined in one operation)
Filtration of suspensions in a wide range of solid particle sizes: from fine (less than 40μm) to several millimeters and with various solid to liquid ratios
Due to the horizontal position of filter plates, the filtration process is optimized as the direction of gravity and filtrate movement coincide
Uniform chamber filling
Cake thickness and, respectively, sludge moisture content adjustability in a wide range
Cake washing ability, if necessary
Guaranteed full cake discharge
Flexible selection of construction materials - from carbon steel to stainless steel - depending on the operational requirements
General principle of operation:
Filtration (separation of suspensions into two phases – liquid and solid). The press filter is a batch process plant with a key component being a frame-mounted filter plate block.
Efficiency:
Capacity, kg/m2*h | Solids content, % | Moisture content, % | Material |
350 | 9.5-10.5 | Cu-Ni conc. | |
830-850 | 7.5 | Zn conc. | |
90 | 20 | Zn leach residue | |
72 | 20 | ZnO leach residue | |
100 | 17-21 | Zn leach residue | |
230 | 12.5 | Сu conc. | |
320 | 14 | Talc | |
90 | 15-20 | Scrubber slurries Pb Zn sulfides | |
200 | 150÷300 g/l | 19÷22 | 4A zeolite |
250÷280 | 50% | 7÷8 | sulfur concentrate |
120 | 50% | 30 | molten sulfur |
35 | 50% | 15÷20 | molten lead compounds |
320 | 600 g/l | 8÷9 | copper smelting slags |
100÷150 | 5%÷10% | 28÷35 | calcium sulfate in wastewater |
200÷250 | 40% | 14÷18 | gold-bearing rock waste |
23÷69 | 15%÷20% | 29÷32 | super fine aluminum hydroxide |
360 | 50%÷65% | 9.78 | copper-nickel concentrates |
300÷400 | 45%÷50% | 7.6 | copper concentrates |
200 | 45%÷50% | 8 | nickel concentrates |
122÷150 | 10% | 20÷25 | molten tantalum-niobium |
300 | 10% | 11.3 | K-acids |
280 | 30%÷35% | 16÷17 | coal sludge |
300 | 40% | ≤9 | iron slags |
220 | 20%÷30% | 12÷18 | gold-bearing rock flotation waste |
160÷180 | 30% | 32 | modified starch |
90 | 12 | mannitol | |
72 | 57% | 20 | zinc oxide choose powder |
257 | 50,50% | 18÷20 | leaching of zinc residues |
65÷75 | 50% | 30÷40 | arsenic sulfide |
200÷220 | 30% | 32 | starch |
Main filtration process stages:
1. Filtration
Process pulp is pumped simultaneously into all filter chambers. Cake starts to accumulate, while filtrate is displaced by the next portion of pulp entering the chamber. As the cake accumulates, the pump pressure increases, and filtrate is squeezed through the cloth until the required cake thickness is reached.
2. Pressing
Water or high-pressure air automatically fills the above-membrane space at the top of each chamber, reducing the chamber volume and compressing the cake to remove additional filtrate. This cake filtration process and a tightly woven filter cloth provide extra pure filtrate, while high pressure maximizes the filtration efficiency. Membrane pressing results in a homogeneous dewatered cake of uniform thickness with minimum residual moisture, which makes its washing with water and blowing with air easier.
3. Cake washing (optional)
Wash fluid is fed through the suspension feed pipe for solid cake washing and removal of dissolved substances.
4. Re-pressing (optional)
Repetitive pressing evenly pushes the wash fluid through the cake layer and removes it.
5. Air blowing
Compressed air is blown through the cake for final dewatering. The moisture content is reduced to a minimum. This process can be fine-tuned by changing the blowing pressure and duration.
6. Cake discharge and cloth washing
After plate block opening, the dewatered cake is removed from each chamber by a movable filter cloth. A built-in high-pressure washing unit sprays fluid on both sides of the cloth for minimum clogging and uniform filtration.
Name / Description | Total filtering area, m2 | Number of chambers, ea. |
|---|---|---|
TPF-100 | 100 | 14 |
TPF-85 | 85 | 12 |
TPF-70 | 70 | 10 |
TPF-55 | 55 | 8 |
Marking:
TPF-100
Tower Press Filter 100 – filtering area, m2
Tower Press Filter
Optional equipment: (to be supplemented)
1. Sensors:
Load cells | Cake weight |
Pressure sensors | Feed, pressing, cake wash, cloth wash, hydraulic system |
Position sensors | Hydraulic cylinder shift, cloth position, cloth drift |
Flowmeters | Feed, air, water, filtrate |
Turbidimeter | Filtrate turbidity |
Temperature sensors | Liquids and air |
Density meter | Cake height adjustment |
2. Air and filtrate separation tank
3. Pulp conditioning tank with agitator
4. Pumping equipment
5. Compressor station
Веб-форма не найдена.